-
Key Takeaways
-
What Is an IMU Calibration?
-
Why Is the IMU Important?
- Safety
- Stability
- Exact Positioning
- Data Quality
-
Understanding the IMU
- Components of an IMU
-
IMU Sensor Fusion
-
IMU Calibration Errors
- Orientation Inaccuracy
- Drifting
- Flight Instability
- Altitude Inaccuracy
- Degraded Maneuverability
- Degraded Battery Efficiency
-
How to Calibrate an IMU
- Step 1: Preparation
- Step 2: Power on the Drone
- Step 3: Select IMU Calibration
- Step 4: Follow on Screen Instructions
- Step 5: Keep the Drone Stable
- Step 6: Wait for Calibration Completion
- Step 7: Confirmation of Calibration
- Step 8: Power Cycle (Optional)
- Step 9: Pre-Flight Check
- Step 10: Taking Flight
-
Advanced Calibration Techniques (Optional)
- Temperature Compensation
- Benefits of Temperature Compensation
- Sensor Bias Correction
- Benefits of Correcting Sensor Biases
-
Conclusion
An important aspect of drone operations is calibrating your drone’s Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU).
Calibration may seem technical and mundane, but it helps to transform your drone from a machine into a precise instrument.
In this article, we’ll delve into the world of IMU calibration and explain what the IMU is, why it’s important, and how to calibrate it correctly.
Key Takeaways
- An IMU is an electronic device that acts as the “sensory system” of a drone. It provides data about the drone’s position, orientation, and movement.
- Over time, errors can accumulate in the IMU’s sensors. Calibrating the IMU corrects these errors, ensuring your drone flies accurately.
- Before taking your drone to the skies, you must go through the IMU calibration process. This is usually a guided step-by-step procedure.
- Advanced calibration techniques are performed in a lab during drone manufacturing or when building a custom drone.
What Is an IMU Calibration?
The IMU is the brain behind your drone’s stability. It consists of accelerometers and gyroscopes that detect changes in pitch, yaw, and roll. When your drone tilts or rotates, the IMU ensures it knows its orientation relative to the Earth.
Over time, errors can accumulate in these sensors. Calibrating the IMU corrects these errors, ensuring your drone flies accurately.
Think of it like tuning a musical instrument; without regular adjustments, its performance can go off-key.
Why Is the IMU Important?

In the realm of drone operations, the significance of reliable flight information cannot be overstated.
Just imagine a pilot trying to navigate his airplane through terrain while blindfolded with no instruments.
For drone operators, accurate flight information is the eyes and ears of their drones and ensures stable flight.
The IMU plays a pivotal role in providing the following:
Safety
Safety is paramount when operating drones.
Precise flight information allows drones to avoid collisions, maintain a distance from obstacles, and respond promptly to changes in the environment.
Stability
A drone’s stability is its defining characteristic.
Reliable flight data guarantees that the drone remains level in conditions or during complex maneuvers. This stability ensures smooth photography and videography while preventing accidents caused by sudden tilts or rolls.
Exact Positioning
Whether for surveying, mapping, or search and rescue missions, precise positioning is essential.
Accurate flight information is crucial for determining location, guaranteeing the accuracy of every data point or executed task.
Data Quality
Drones are not merely flying cameras; they serve as data collectors. Accurate flight information ensures the trustworthiness and precision of the gathered information.
Understanding the IMU
An Inertial Measurement Unit, also known as an IMU, is an electronic device that acts as the “sensory system” of a drone. Its primary role involves monitoring and providing data about the drone’s position, orientation, and movement.
An IMU ensures that the drone maintains stability, responsiveness, and optimal flight performance.
Components of an IMU
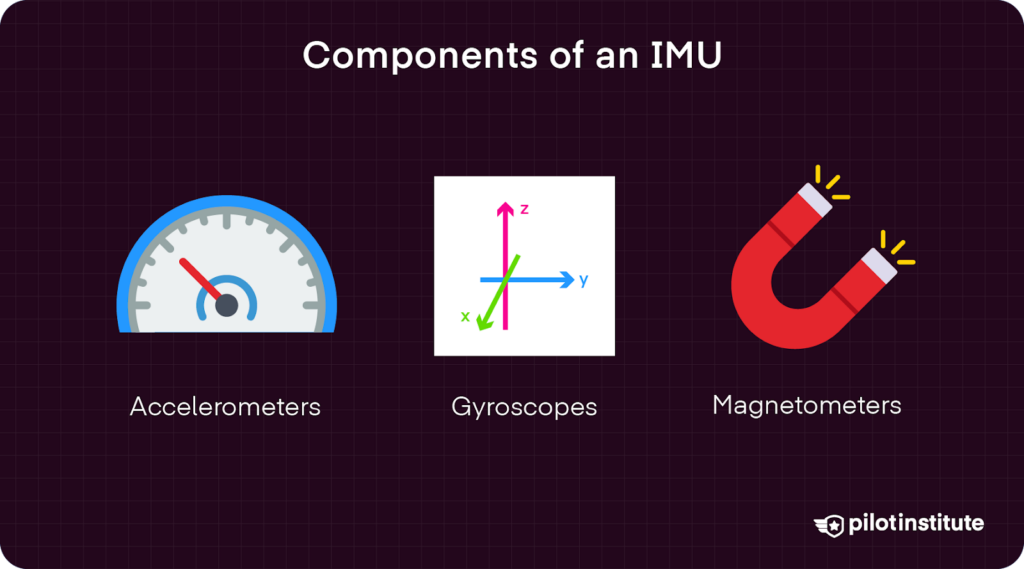
Accelerometers
Accelerometers are responsible for measuring linear acceleration, including changes in velocity and tilt angles. They utilize the principles of inertia to detect variations in motion.
When the drone accelerates or tilts, an internal mass within the accelerometer resists these changes. This resistance is then converted into signals that indicate the drone’s movement.
Gyroscopes
Gyroscopes measure velocity or rotational movement. Think of it as the drone’s internal balancing act.
As the drone maneuvers through the air, the gyroscope detects changes in its orientation, specifically its roll, pitch, and yaw.
By constantly monitoring these rotations, the gyroscope provides real-time feedback to the drone’s control system, allowing it to maintain stability.
Magnetometers
Magnetometers determine the drone’s heading or orientation to Earth’s magnetic field. They detect Earth’s magnetic field and utilize it to establish the drone’s heading.
They play a crucial role in ensuring correct positioning during flight.
Barometer
The barometer doesn’t usually form part of the IMU. Instead, it works with the IMU to provide more accurate altitude information.
The purpose of a barometer is to gauge atmospheric pressure, which gives us information about the drone’s altitude above sea or ground level.
As the drone goes up or down, barometers detect changes in air pressure. By comparing this pressure to sea level pressure, we can determine the drone’s altitude (either MSL or AGL).
Some drones use infrared or GPS technology to measure altitude instead.
IMU Sensor Fusion
With so many sensors providing information about the drone, we need a way to bring it all together.
“Comprehensive data integration” involves combining the information from accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers.
Together, they form the IMU, which provides information about the drone’s movement and position.
This integration process, known as “sensor fusion,” allows the IMU to compensate for the strengths and weaknesses of each sensor.
The IMU continuously analyzes data to ensure that the drone can make real-time adjustments for stability, follow flight paths accurately, and execute maneuvers precisely.
IMU calibration fine-tunes these sensors, allowing them to work together seamlessly.
IMU Calibration Errors
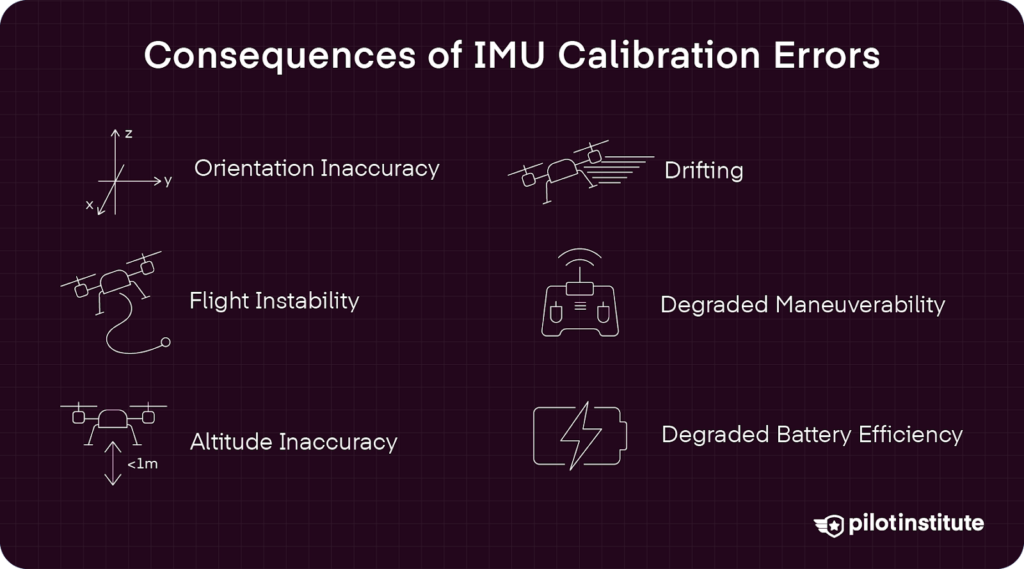
Calibration errors in drones can have severe effects on their performance. Any error during the calibration process can lead to issues that compromise flight accuracy and stability.
Here are the potential consequences.
Orientation Inaccuracy
When calibration errors are present, the drone may misinterpret its orientation.
The drone might mistakenly believe it is level when it’s actually tilted. It could think it’s facing one direction when it’s actually pointing elsewhere.
This can result in erratic flight behavior, making it challenging for the pilot to control the drone effectively.
In some cases, these errors can even lead to crashes.
Drifting
Calibration errors can introduce drift, causing the drone to gradually deviate from its intended course or position.
This becomes particularly problematic when performing tasks that require positioning or capturing of aerial footage. It can also affect data collection accuracy or cause shaky video footage.
Flight Instability
Errors in calibrating gyroscopes and accelerometers can cause the drone to lose stability during flight.
Unstable flight may result in uncontrollable tilting, rolling, or flipping motions. This not only risks damaging the drone but also poses safety hazards to people and property on the ground.
Altitude Inaccuracy
Incorrect IMU calibration can impact altitude readings. Inaccurate altitude readings increase the risk of collisions or airspace violations.
Degraded Maneuverability
Another difficulty arises when calibration errors affect the drone’s ability to perform accurate maneuvers like turns or hovering.
These maneuvers are crucial during search and rescue missions, surveying tasks, and inspections. Calibration errors can hinder the effectiveness of these operations.
Degraded Battery Efficiency
Drones with calibration errors may overcompensate for perceived imbalances, leading to increased energy consumption and reduced flight time.
How to Calibrate an IMU
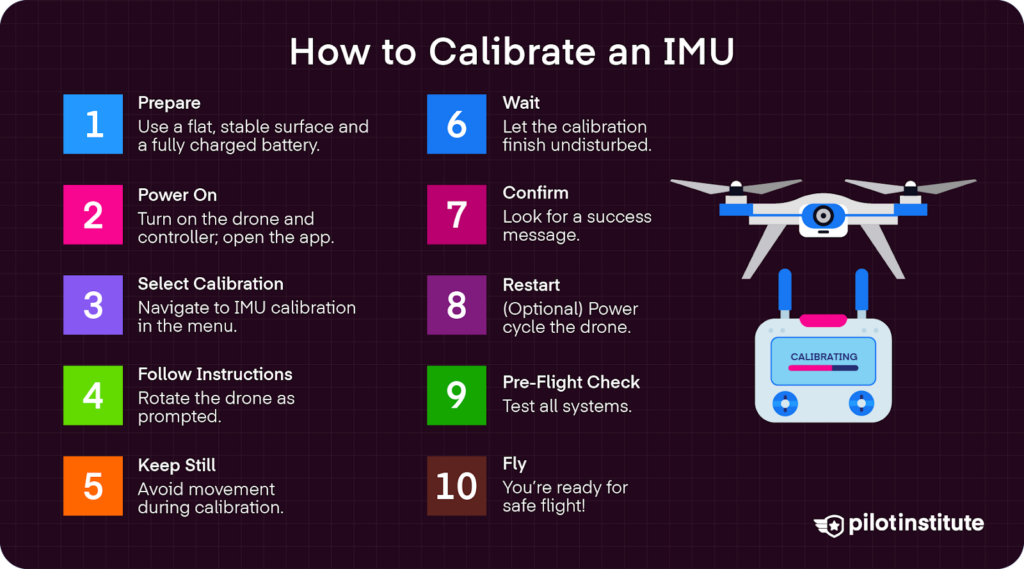
Before taking your drone to the skies, you must go through the IMU calibration process.
Here’s a step-by-step overview of how to calibrate your IMU.
Step 1: Preparation
Choose a location where your drone can rest on a level and stable surface during calibration.
Make sure your drone’s battery is charged to complete the calibration process without any interruptions.
Step 2: Power on the Drone
Turn on both your drone and remote controller, allowing them to establish a connection.
Open your companion app or use your controller to navigate to the settings or calibration menu of your drone.
Step 3: Select IMU Calibration
Look for and choose the option that allows you to calibrate the IMU. The specific steps may vary depending on your drone model and its firmware.
Step 4: Follow on Screen Instructions
Your drone’s app or controller should provide step-by-step instructions for performing the calibration process. Follow the instructions displayed on your screen.
As part of the calibration process, you will usually need to gently place the drone on its side, back, and top while it records sensor data.
[Post Banner: Drone News Update]
Step 5: Keep the Drone Stable
It’s crucial to keep the drone as steady as possible during calibration to avoid any errors caused by movement or vibrations.
Some drones may require you to rotate them smoothly along axes as instructed.
Step 6: Wait for Calibration Completion
Allow the drone time to complete the calibration process, which can take a couple of minutes.
Do not disturb the drone while it is undergoing calibration.
Step 7: Confirmation of Calibration
Once calibration is finished, your drone will typically display a message confirming completion. In some models, you may need to confirm that calibration was successful.
Step 8: Power Cycle (Optional)
Depending on the drone, it is recommended that you power off and restart your drone after calibration to ensure that the new settings are in effect.
Step 9: Pre-Flight Check
After completing calibration, perform a pre-flight check of all systems to ensure they are functioning correctly and that the drone responds as expected.
Step 10: Taking Flight
Once you’ve confirmed that the IMU is correctly calibrated, you can proceed with confidence knowing that your drone is ready for safe and stable flight.
It’s worth noting that the specific steps and procedures for calibration may vary depending on the make and model of your drone.
To ensure accuracy, it’s always recommended to consult your drone’s user manual and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for guidance on the IMU calibration process.
Regular calibration is highly advised by manufacturers as it plays a vital role in maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safety throughout your drone flights.
Advanced Calibration Techniques (Optional)
Advanced calibration techniques are typically performed in a lab during drone manufacturing or when building a custom drone and IMU.
Some of these advanced techniques happen automatically through the drone’s software.
Temperature Compensation
Temperature fluctuations can impact the accuracy and sensitivity of IMU sensors. It is crucial to account for these effects to ensure accurate drone operations.
Here’s how temperature compensation works.
Calibration Across Temperatures
Manufacturers typically calibrate IMU sensors under controlled lab conditions. However, it’s important to note that these calibrations may not cover the temperature ranges that drones experience during real-world operations.
Temperature Sensing
Advanced IMUs often incorporate temperature sensors to continuously monitor temperatures during flight.
Thermal Modeling
Drone software utilizes thermal modeling techniques to estimate how temperature affects sensor readings. This helps with the real-time correction of any errors caused by temperature variations.
Temperature Profiles
IMUs can store temperature profiles that allow sensor outputs to be adjusted based on operating conditions. These profiles are usually provided by the manufacturer and cover a range of temperatures.
Real-Time Adjustment
During a flight, the IMU can utilize the thermal model and temperature profiles to make real-time adjustments to the sensor data. This ensures accurate readings regardless of any fluctuations in temperature.
Benefits of Temperature Compensation
Improved Accuracy
By compensating for temperature variations, we minimize errors. This ensures that the IMU consistently provides reliable data throughout a drone’s flight regardless of weather conditions.
Stable Performance
When exposed to changes in temperature, drones can maintain stable flight and accurately determine their positioning.
Sensor Bias Correction
Sensor bias correction is a technique used to rectify errors or biases in sensor measurements.
These biases can arise due to manufacturing imperfections or other factors resulting in inaccuracies in the IMU data.
Estimating Biases
Prior to a flight, the drone’s software estimates sensor biases by comparing sensor measurements with known reference data.
Data Fusion
IMUs often utilize sensor fusion techniques that combine data from sensors like accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers. Sensor fusion helps correct biases effectively.
Calibration Parameters
The drone software stores calibration parameters that take into account sensor biases. These parameters are then applied to the sensor data to correct any bias effects.
Continuous Monitoring
While the drone is in flight, the IMU constantly monitors sensor data and makes real-time adjustments based on estimated biases.
Benefits of Correcting Sensor Biases
Enhanced Accuracy
By correcting sensor biases, the IMU ensures that the data it provides is as precise and accurate as possible. This minimizes errors in orientation, positioning, and movement.
Improved Stability
Correcting biases also improves the drone’s stability, making it more responsive to pilot commands and reducing erratic behavior.
Both temperature compensation and sensor bias correction are techniques that greatly contribute to the reliability and precision of IMU-calibrated data for drones.
These methods are particularly valuable for professional-grade drones used in applications where precision is crucial, such as mapping, surveying, and inspections.
Manufacturers and software developers continuously refine these techniques to enhance drone performance and ensure data.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve dived deep into the world of IMU calibration, have a look at our commercial drone courses.
Our courses will help you achieve success as a commercial drone pilot. Pass the Part 107 test, take to the skies, and start earning.





