-
Key Takeaways
-
Types of Loans Available for Flight School
- Federal vs. Private Loans
- Pros
- Cons
- Pros
- Cons
- Aviation Lenders
- Personal Loan
-
Eligibility Requirements for Flight School Loans
- Use a Co-Signer
-
How to Apply for a Flight School Loan
- Choose the Right Lender
-
Tips to Minimize Loan Costs
- Work Part-Time
- Use Loan Funds Wisely
-
Pros and Cons of Taking Out a Loan for Flight School
- Pros
- Cons
-
Conclusion
Becoming a pilot is super exciting, but it can also cost a lot of money. For most people who want to be pilots, taking out a loan is the only way they can pay for their education and start flying.
Did you know there are specific loans just for flight training? These loans are from private lenders and aviation organizations that understand how expensive pilot training can be.
This guide will tell you how to get a loan for flight school, what you need to qualify, and ways to save money while pursuing your dream of becoming a pilot.
Ready to find out? Great!
Key Takeaways
- Federal student loans offer lower rates and better terms than private loans.
- Aviation lenders like AOPA Finance and Meritize provide tailored options.
- Flight school loans need a 670+ credit score and stable income or a co-signer.
- Scholarships, part-time work, and budgeting lower loan costs.
Types of Loans Available for Flight School
As an aspiring pilot, your journey to the cockpit may begin with exploring financing options.
So, which type of loan is right for you?
Start with federal student loans or aviation lenders, as they generally provide lower interest rates compared to private loans.
Federal vs. Private Loans
Federal loans are only available if you are enrolled in a degree program at an accredited aviation college. Typically, Part 61 flight schools do not qualify for federal aid.
Federal student loans should be your first stop. Why? They typically offer:
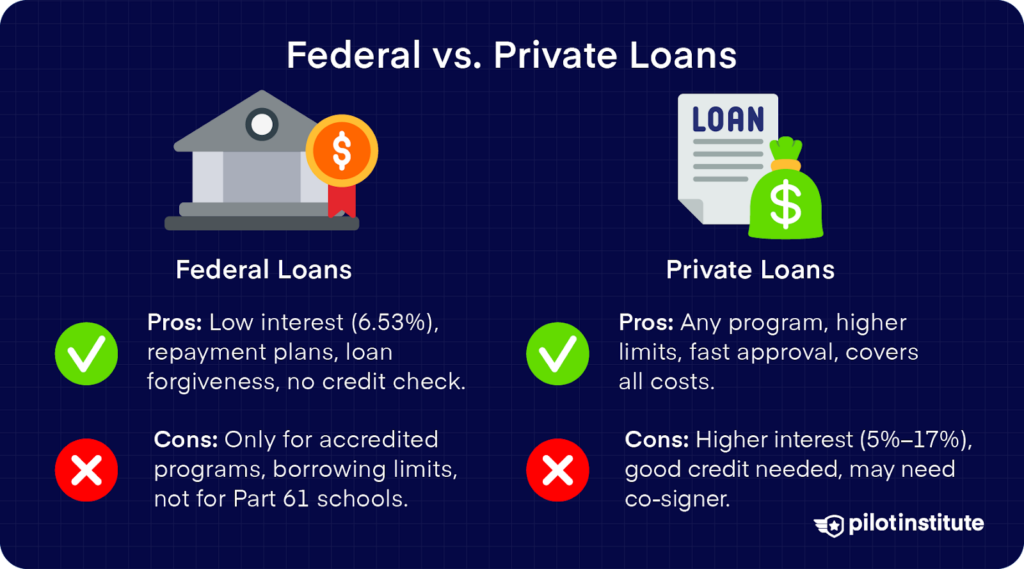
Federal Loans
Pros
-
Lower interest rates (5-6.53%) than private loans.
-
Income-driven repayment plans.
-
Potential loan forgiveness options.
-
No credit check for most undergraduate loans.
Cons
-
Only available for accredited aviation degree programs.
-
Annual and lifetime borrowing limits.
-
Not available for Part 61 flight schools unless they’re part of an accredited program.
-
Must maintain satisfactory academic progress.
If federal loans are not an option, private loans from banks and credit unions can help, although they often have higher interest rates. But what exactly should you expect from a private loan? Let’s examine the pros and cons.
Private Loans
Pros
-
Available for any flight training program.
-
Higher borrowing limits.
-
Faster approval process.
-
Can cover all flight training costs.
Cons
-
Higher interest rates (typically 5% – 17%).
-
Usually requires good credit (670+ score).
-
May need a co-signer.
-
Fewer repayment options.
Aviation Lenders
There are several lenders that focus on aviation training loans. Why choose an aviation-specific lender over a regular bank? These lenders are familiar with the costs and career paths in aviation, which can be beneficial for you.
- AOPA Finance collaborates with regional banks to provide competitive rates for flight training.
- Sallie Mae offers career training smart option loans specifically designed for aviation.
- Meritize takes into account your educational background along with traditional credit criteria.
The interest rate varies based on the lender, from 3.49% (fixed) to 5.04% (variable) at Salli Mae and 7.1% to 9.99% for AOPA. Contact lenders for accurate estimates.
Personal Loan
Don’t qualify for aviation-specific loans? If you don’t qualify for an aviation loan, consider taking a personal loan as a backup. Online lenders like SoFi and LendingClub provide unsecured personal loans for flight training but have higher interest rates (up to 14%) and a one-time 5% origination fee.
Eligibility Requirements for Flight School Loans

To qualify for aviation loans, you need to meet some basic criteria. What do lenders look for in loan applicants? A lender needs to assess your risk level and consider various factors to evaluate your creditworthiness.
Most aviation lenders look for:
- A minimum credit score of 670 for private loans.
- Higher scores (700+) for better interest rates.
- Have income to pay back the loan.
- Clean credit history with no major negative marks.
Lenders prefer to see a stable income and a debt-to-income ratio that is 36% or less. Typically, you should have at least two years of employment history and be prepared to provide pay stubs or tax returns as verification.
Use a Co-Signer
What if my credit score isn’t high enough? If you have no credit history or low credit, you may need a co-signer to secure a loan. While parents frequently act as co-signers, anyone with good credit can assist you.
A co-signer can:
- Help you qualify for loans.
- Secure better interest rates.
- Increase your approval chances.
Note: As a loan applicant, your credit history and current financial status can impact the eligibility and approval process.
How to Apply for a Flight School Loan

Getting your pilot’s license starts with smart financing. The loan application process is straightforward if you properly prepare and gather the necessary documents. Doing so will make your journey to financing your flight training much easier.
Ready to apply? Here’s your loan checklist.
Choose the Right Lender
Before selecting a lender, it’s important to compare interest rates, loan terms, origination fees, prepayment penalties, and deferment options. What else should you do? Get quotes from at least three different lenders to get the best deal.
Compare these factors:
- Interest rates (fixed vs. variable).
- Loan terms (5-20 years typical).
- Origination fees.
- Prepayment penalties.
- Deferment options.
Application Process Overview
The application process involves collecting several documents, including a government ID, proof of income, bank statements, and a breakdown of flight school costs. Let’s take a look at the process.
1. Gather required documents:
-
-
-
- Government ID.
- Proof of income.
- Bank statements.
- Flight school costs.
-
-
2. Submit applications.
3. Review and compare offers.
4. Accept the best terms and sign the paperwork.
Approval and Disbursement Timelines
After you submit your applications, lenders generally take about a few weeks to review your application, make a decision, and disburse the funds. It’s best to start the loan process at least a month before your training begins.
Most lenders take 2-3 weeks to:
- Review your application (3-5 business days).
- Make a decision (1-2 weeks).
- Disburse funds (5-7 business days after approval).
Tips to Minimize Loan Costs

Although flight training involves a large financial commitment, there are some strategies you can use to lower your total expenses. Wondering where to start? Let’s explore some of your different options.
Scholarships and Grants
Need to save some money? Take a look at scholarships and grants, which are essentially free funds that you won’t need to pay back. Make sure to apply early, as many scholarships have spring deadlines, with awards distributed in the fall.
Look into:
- AOPA Foundation scholarships.
- Women in Aviation International grants.
- EAA aviation scholarships.
- Local flying club awards.
Work Part-Time
Consider taking up a part-time job at your flight school. What jobs are available at flight schools? Many schools offer work-study programs, dispatch desk jobs, or ground school teaching assistant positions. These jobs build experience and may lead to discounts on flight training.
Use Loan Funds Wisely
How can you stay on budget during training? To make your loan funds last longer, create a detailed budget. Whenever possible, buy used books and materials, and consider purchasing block time for better rates.
These are some tips on using your loan funds:
- Create a detailed training budget.
- Track all expenses.
- Buy used books and materials when possible.
- Consider block time purchases for better rates.
- Keep emergency funds separate from training funds.
Pros and Cons of Taking Out a Loan for Flight School

Before committing to a flight school loan, take a look at all the benefits and drawbacks. Is taking out a loan worth it? Remember that signing a loan agreement can impact your financial future, so choose wisely.
Pros
Taking a loan for flight school has many benefits. This biggest advantage is that you can kickstart your aviation career without having to wait until you’ve saved the entire amount.
Benefits:
- Start your aviation career sooner.
- Flexible payment options spread costs over time.
- Potential tax benefits from interest payments.
- Build credit history while pursuing your dream.
Cons
What are some drawbacks? High interest rates can increase your training expenses, as repayment terms can last as long as 20 years. Also, if your aviation career doesn’t go as planned, you might end up with a hefty debt.
Drawbacks:
- High interest rates increase the total cost.
- Long repayment terms (often 10-20 years).
- Monthly payments can strain early-career budgets.
- Risk of debt if career plans change.
Note: It’s important to research starting salaries based on your career path, such as a Flight Instructor or a First Officer at a regional airline, to make sure that you can pay off your loan on time.
Conclusion
Securing a loan for flight school can be a powerful tool to jump-start your aviation career, but you need to approach the process thoughtfully.
Truly understand your options, compare lenders, and consider additional financial support like scholarships. Remember, the right loan will support your training without creating unnecessary financial strain down the line.
Plan carefully and budget wisely. Then, you’ll be on your way to achieving your aviation dreams while keeping your financial future clear for takeoff.